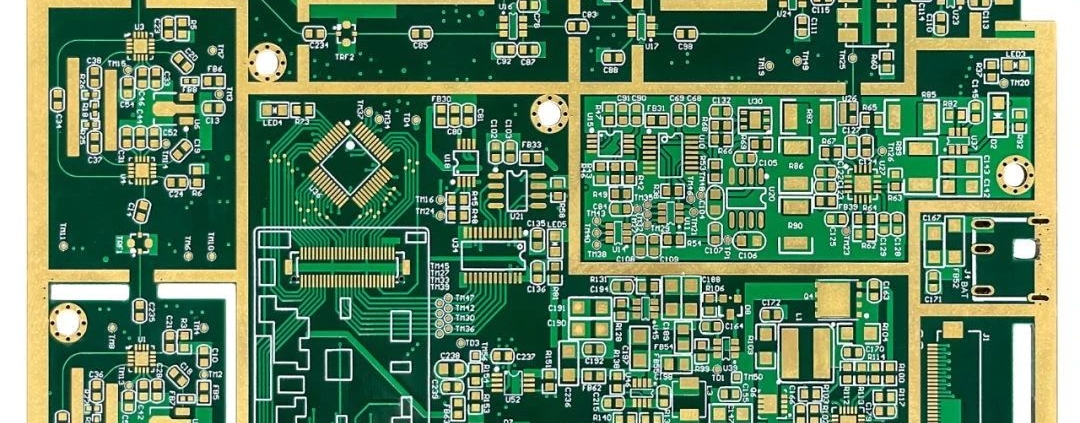
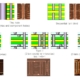
Is the circuit board covered with grid copper or solid copper?
The so-called copper pouring is to use the idle space on the circuit board as the reference plane and then fill it with solid copper. These copper areas are also called copper filling.
The significance of copper coating is to: reduce the impedance of the ground wire and improve the anti-interference ability; reduce the voltage drop and improve the power efficiency; and connect to the ground wire to reduce the loop area.
Also for the purpose of keeping the PCB from deforming as much as possible during welding, most PCB manufacturers will also require PCB designers to fill the open areas of the PCB with copper or grid-like ground wires. If the copper is not handled properly, it will The gain outweighs the loss. Does copper coating have “more pros than cons” or “does more cons than pros”?
Everyone knows that at high frequencies, the distributed capacitance of the wiring on the printed circuit board will work. When the length is greater than 1/20 of the corresponding wavelength of the noise frequency, the antenna effect will occur, and the noise will be emitted outward through the wiring. If there is poorly grounded copper in the PCB, the copper becomes a tool for transmitting noise.
Therefore, in high-frequency circuits, do not think that the ground wire is connected to the ground somewhere. This is the “ground wire”. You must drill holes in the wiring with a spacing of less than λ/20, and connect it to the ground. The ground plane of the shelf is “well grounded”. If the copper coating is handled properly, the copper coating not only increases the current, but also plays the dual role of shielding interference.
There are generally two basic methods of copper pouring, namely large-area copper pouring and grid copper pouring. People often ask whether it is better to pour copper pouring over a large area or with grid copper pouring. It is difficult to generalize.
why? Covering a large area with copper has the dual functions of increasing current and shielding. However, if a large area of copper is covered with wave soldering, the board may warp or even blister. Therefore, when covering a large area with copper, several grooves are usually opened to alleviate blistering of the copper foil.
Simple grid copper coating mainly has a shielding effect, and the effect of increasing current is reduced. From the perspective of heat dissipation, the grid is beneficial (it reduces the heating surface of copper) and plays a certain role in electromagnetic shielding.
It should be pointed out that the grid is composed of traces in staggered directions. We know that for circuits, the width of the traces has its corresponding “electrical length” for the operating frequency of the circuit board (the actual size divided by The digital frequency corresponding to the working frequency is available, please refer to relevant books for details).
When the operating frequency is not very high, perhaps the role of the grid lines is not very obvious. Once the electrical length matches the operating frequency, it is very bad. You will find that the circuit cannot work properly at all, and interference is being emitted everywhere. signal of.
The suggestion is to choose based on the working conditions of the designed circuit board, and don’t stick to one thing. Therefore, high-frequency circuits have multi-purpose grids that require high interference resistance, and low-frequency circuits have high-current circuits and other circuits that commonly use complete copper laying.