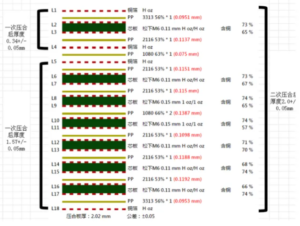
How to effectively deal with common quality problems of HDI circuit boards?
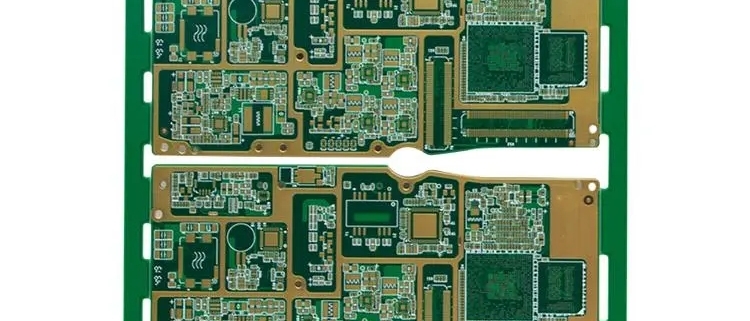
In the rapidly developing field of electronic manufacturing, high-density interconnect (HDI) circuit boards have become the core components of many electronic products due to their excellent performance and wide application. However, HDI circuit boards often encounter some quality problems during the manufacturing process. How to effectively deal with these problems is the key to improving product quality and ensuring market competitiveness.
Common quality problems and causes
Circuit breakage and short circuit: Due to the high integration and precision design of HDI boards, the circuit spacing is small, and the slightest carelessness during processing may cause circuit breakage or short circuit.
Poor welding: Problems such as loose welding points, cold welding, etc. will seriously affect the electrical performance and reliability of HDI boards.
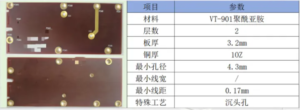
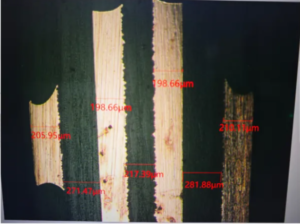
Material problems: The quality of materials such as substrate materials, copper foil, and solder mask ink is unstable, which will lead to the overall performance of HDI boards.
Improper process control: Improper control of key processes such as etching, drilling, and electroplating will also lead to quality problems.
Effective response strategy
Optimized design and reasonable process design: Fully consider the characteristics of HDI boards in the design stage, reasonably layout the circuits, and avoid overly compact designs.
Process optimization: According to the characteristics of HDI boards, optimize key processes such as etching, drilling, and electroplating to ensure processing accuracy and stability.
Strict material screening and control Supplier selection: Select reputable and quality-guaranteed suppliers to ensure the quality of raw materials. Material testing:
Strictly test the raw materials entering the factory to ensure that they meet the standards. Strengthen process control and quality testing Process monitoring: Establish a complete process control system to monitor and record key processes in real time. Quality testing: Introduce advanced testing equipment to conduct comprehensive and detailed quality testing of HDI boards.
Improve employee skills and awareness Skill training: Strengthen employee skills training to improve employees’ understanding and response capabilities to HDI board quality issues. Quality awareness: Improve employees’ quality awareness so that every employee understands the importance of quality.
Establish a quality management system System establishment: Establish a complete quality management system, from design, raw materials, production to testing, each link has clear standards and processes. Continuous improvement: Through regular quality reviews and internal audits, problems are discovered and continuously improved.
The response to HDI circuit board quality issues requires us to start from multiple aspects, including optimizing design and process, strict material screening and control, strengthening process control and quality testing, improving employee skills and awareness, and establishing a quality management system. Only in this way can we ensure that the quality of HDI circuit boards is stable and reliable and meets market demand.